Enterprise Cloud Computing Vs. Cloud Computing – Examples & More!

Ever wondered how the work in today’s corporate space is operationally tidy and uniform? It hasn’t been the case since its inception – many mistakes have led to the current smooth workflow. Enterprise cloud computing is one element of the modern workspace that makes modern corporate offices workable.
You may have heard the term digital era and may even know that the fourth IR depends on this trend. The rapid technological advancements push sectors to match the pace and be on the same page for proper regulatory change management.
The following article will focus on the system and how it contributes to the modern workspace – enhancing security and productivity for the organization. The article will also explore how cloud computing and enterprise cloud computing differ. Ready to find out?
What is Enterprise Cloud Computing?

Enterprise cloud computing is a model that helps organizations (enterprise kinda gave it away). The model allows enterprises to access virtualized IT resources through the internet on a paid model.
Enterprise cloud computing has a rich resource, which includes data processing power, increased data storage, capabilities of virtualization, and servers that make seamless work possible.
Enterprise cloud computing also allows the organization to stay in the loop with the latest regulatory technology. Think of this model as a unified environment where everything about IT is ready for access.
This is the single point of control for managing infrastructure and applications across clouds – an amalgamation of private and public clouds. Enterprise cloud computing provides your company with the best of both worlds by enhancing security without the hassle of maintaining different cloud computing systems.
This is an excellent solution for enterprises with a vast workforce and accessing IT resources is difficult. Both private and public clouds and distributed infrastructure characterize these.
Using virtualization technologies, enterprise cloud computing creates virtual machines within resources. These machines allow physical servers to run on various separate machines with varying operating applications and systems.
These resources are available to customers through a stable and secure internet connection. Consequently, they can efficiently use a resource and improve scalability as customers access resources on demand.
Finally, the enterprise cloud model delivers the advantages of public offerings for enterprise applications without compromising the value of private data centre environments. So, how does it differ from cloud computing? Let’s explore!
What is Enterprise Cloud Computing Vs. Cloud Computing

The differentiating term between the two models is enough to tell you about the primary difference between the two. Nevertheless, here’s what differentiates enterprise cloud computing and cloud computing.
Standard cloud computing involves public or private cloud resources that use both clouds and a distributed cloud infrastructure. This distributed infrastructure is just public cloud infrastructure in multiple locations.
A unified IT environment offers centralized management and control – that’s how the enterprise model differs from its counterpart.
| Criteria | Enterprise cloud computing | Cloud computing |
| IT environment | Unified IT environment that offers centralized control | Does not have a unified environment |
| Cloud types | Combines private, public and distributed clouds | Can use either private or public cloud models |
| Use case | A unified IT environment that offers centralized control | File storage, big data analytics, enterprise data integration, software development and testing |
How Does Enterprise Cloud Computing Work?
Enterprise cloud computing uses a combination of different models – I’m sure it’s been clear now. This unified IT environment allows businesses to access IT resources on demand. Be it storage, identity management, or processing power – at the tip of their fingers – more like their cursor, you get it.
Here are the different elements that make this cloud computing model work:
- The enterprise cloud computing model provides centralized control for businesses to manage applications and infrastructure in their day-to-day operations.
- The model also provides virtualization controls, which makes cloud computing possible for businesses. This helps the cloud providers maintain their data centre and create different virtual environments using the underlying hardware resource.
- The model’s scalability allows customers to scale up or down the resources per their business needs.
- The model also offers serverless computing, which offloads back-end infrastructure management to cloud providers, allowing complete focus on the application.
- FaaS, or Function-as-a-service, is a subset of serverless computing that allows developers to run portions of application code in response to specific events. It goes together with the SaaS integration.
That’s how enterprise cloud computing brings computing infrastructure on-premises.
Implementation of Enterprise Cloud Computing
The implementation process includes integrating cloud computing solutions into the IT framework of the organization. The process consists of the following steps:
- Analyzing the organization’s needs includes evaluating the requirements at the moment.
- Selecting the appropriate cloud platform that can meet the organization’s needs.
- Configuring the networking and security so that it is set up correctly for the cloud.
- Setting up the storage solution for the cloud is another essential part of the implementation process.
- Deploying applications to the cloud
- Managing and monitoring the cloud environment for seamless connection
- Migrating data to the cloud for complete access across levels
- Establishing security and compliance for complete adherence
Practices for Your Enterprise Cloud Strategy
If your business is implementing an enterprise cloud strategy, here are the different practices that you should follow:
- Developing a cloud strategy team for the implementation will ensure a smooth process. In addition, there will be a Chief Technology Officer who will lead the strategy development and implementation.
- Creating a cloud strategy framework will help the business make decisions by keeping the best use of resources and objectives in mind. This will help support business continuity and encourage innovation.
- Planning a cloud migration is essential to the process as it helps streamline IT operations, save costs, and accelerate digital transformation.
- Choosing a cloud service that supports the needs is next. You should consider the cloud computing system’s security and compliance, support, and scalability. Moreover, you should note the cost of ownership for the cloud computing software you have chosen.
- Implement data security and compliance with the help of strong access controls, encryption, and regular security audits. It also helps ensure your cloud provider complies with the existing industry regulations and standards.
- Ensure enterprise cybersecurity is in place for complete protection from cyber threats.
- Align cloud initiatives with organization goals to smooth adoption and serve the overall mission and vision.
- Enterprise risk management should also be in place for managing the organization’s risks, including cloud risk management.
Despite being helpful for organizations, it is essential that continuous monitoring of the model is always present. This is because cloud computing can expose the organization to threats such as breaches, account hijacking, and malware, among other things.
Effective risk management strategies will help reduce the likelihood or impact of these risks.
Different Types of Enterprise Cloud Architecture And Their Difference
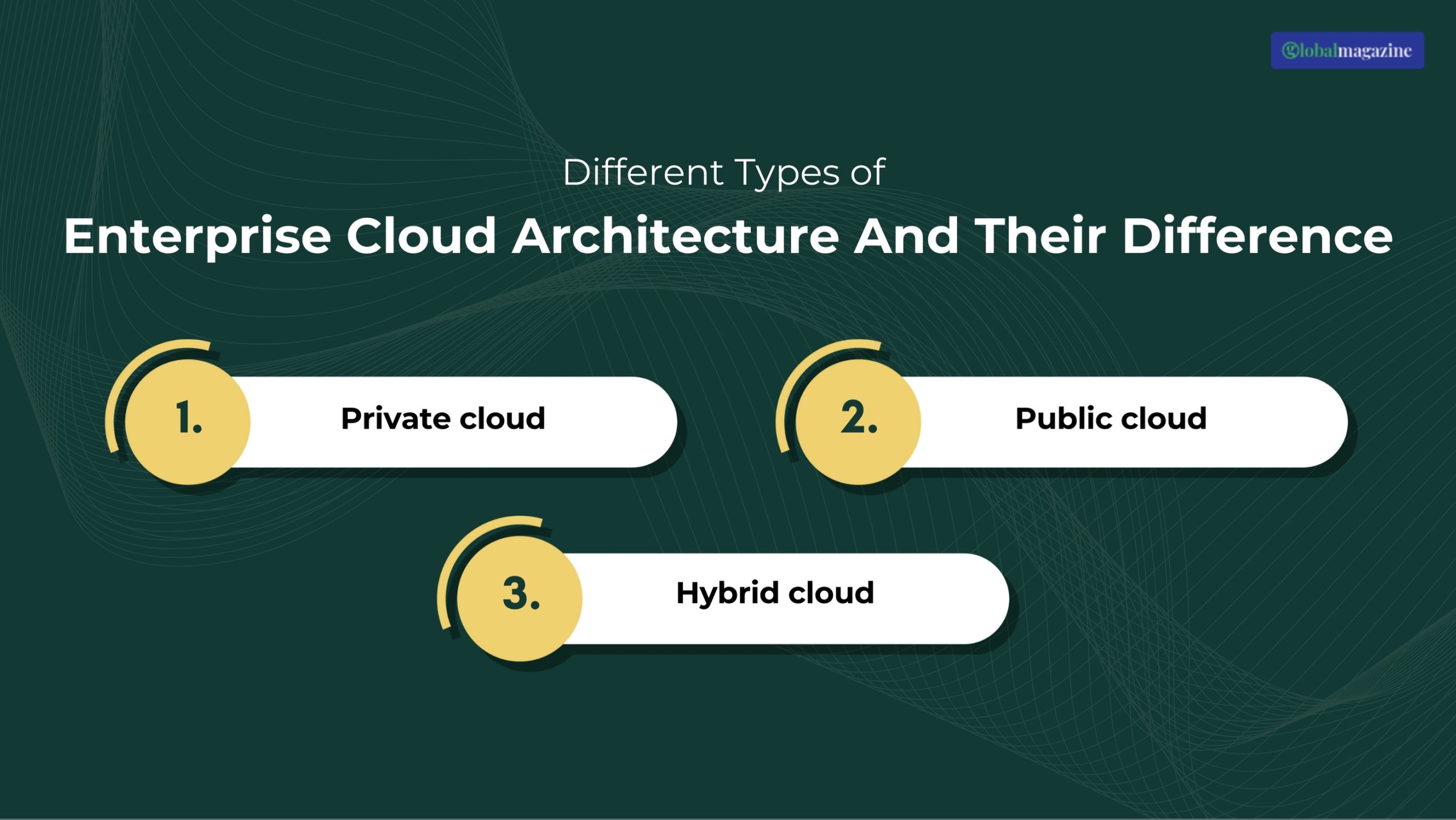
Here are the different types of cloud computing that your organization can browse. Some of those are:
Private Cloud
In this type, the organization owns and manages the cloud-hosted privately on-premises. The private cloud offers more control over the resources and security. However, these are costlier than other types and require more IT expertise.
Public Cloud
This is when a third-party cloud service provider owns the physical infrastructure and operates it and the cloud computing resources. Public clouds are easy to scale without any software or hardware investment. The process uses multi-tenant architectures.
Hybrid Cloud
Finally, the combination of private and public cloud architecture helps businesses use the best services for their business and workload needs. In addition, hybrid clouds are often chosen for companies that want control over the data while taking advantage of the public cloud features.
The other types of cloud computing infrastructure include multi-cloud and high-performance computing cloud. The HPC cloud uses AWS and expedites the workloads. HPC can also be thought of as custom-built supercomputers or computer clusters.
Thus, the main difference between all these types is the level of control, security and cost of ownership/implementation.
Pros, Cons, and Challenges of Enterprise Cloud Computing
Here are the different pros, cons, and challenges of this cloud computing model:
- The data stored online may be vulnerable to unauthorized access. Thus, to ensure security, you must work with a trusted provider who can prioritize cybersecurity.
- The vendor lock-in is pretty brutal with this model. It relies on a single cloud provider, limiting the organization’s ability to switch providers or adopt new technologies. A multi-cloud strategy that can help reduce dependency.
- Compliance issues may come while moving data from internal storage to the cloud. Thus, it is essential that organizations comply with official regulations and laws.
- High cost of ownership due to the additional costs that may come with backing up redundant data
- The scalability of the model is one of the most substantial pros. It helps organizations level up high-performance resources without upfront investments.
- Another one of the challenges that businesses may face with this model is vulnerability to internet outages. As the model depends on internet connectivity, it is prone to reducing productivity for employees.
- Automation reduces the risk, complexity, and operational overhead of managing applications across multiple cloud platforms.
- The cost-efficient solution that prevents vendor lock-in for businesses. It also helps achieve better cost savings by leveraging the competitive pricing of different cloud providers.
- The model operates on a subscription-based payment mode, allowing businesses to avoid high initial costs.
These were all the challenges, pros, and cons of using the cloud computing system for your organization.
Future Trends of This Cloud Computing

The future of enterprise cloud computing looks interesting with all the exciting trends coming its way. Some of these are:
- Edge computing brings resources closer to the users and devices. It reduces latency, enables real-time processing, and is driven by the need for faster data processing. Especially useful in data applications such as IoT, AR/VR, and autonomous vehicles.
- Serverless computing in this model brings new cloud offerings with benefits for software developers as they don’t have to manage and maintain network servers.
- Artificial intelligence in cloud computing will reduce the cost and enhance the effectiveness of the services. It also helps businesses deliver better user experience, increase work efficiency, and provide valuable insights.
- Sustainable cloud computing minimizes environmental impact by optimizing energy consumption, improving resource efficiency, and providing valuable insights.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) will also be an essential part of cloud computing as it connects systems and generates user habits and patterns data.
That was all about the different future trends of the model and how it can bring organizations up to speed with the various innovations in the digital era.
Wrapping It Up!
That concludes the article on enterprise cloud computing and how you can improve your business process. It is also important to note that the enterprise workflow significantly benefits from the model as it helps improve efficiency and collaboration across levels.
With the help of cloud computing, your business can improve adherence to regulatory compliance and laws around technology use and interpretation. This solution is unlikely to be replaced with the trends that could be incorporated within it.
Read More: